Freeing space on your Mac OS X startup disk
- Freeing Up Memory On Mac
- Free Up Storage On Mac El Capitan
- Freeing Up Memory In Vista
- Freeing Up Memory On Mac Air
- Freeing Up Memory On Macbook Pro
This extract from a chapter of our book Troubleshooting Mac® OS X describes several ways to free-up space on your Mac OS X startup disk, also known as your Mac OS X boot volume.
While you could replace your current hard drive with a larger model, or install a second internal hard drive if your Mac will support such, the following tips will help you to free some space without changing your hardware. Additional tips are provided for saving more space if you have a second internal hard drive or an available partition.
Just go to Disk Utility and add another partition and name it whatever you want, just change the file type to FAT32 and then boot into windows and format that logical drive and boom there you go. To free up RAM on your Mac, firstly, you should find out what app uses so much of your memory. The memory-heavy programs are listed in Activity Monitor, Memory tab. If there is an app you aren’t using at the moment, click it and press the “X” sign to quit it.
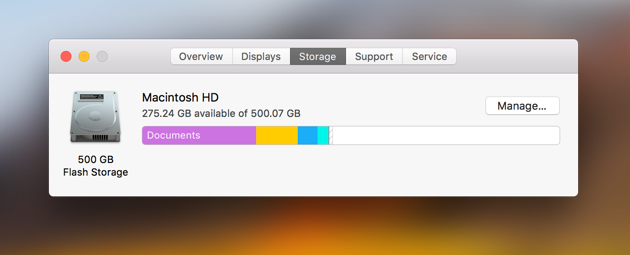
Determining available space on your startup disk
To check how much free space is available on your startup disk:
- In Finder®, select your startup disk's icon. For most users, this is Macintosh HD.
- Press the Command-I keyboard combination.
- The Get Info window for your startup disk will open. In the General pane, the Capacity, Available (free space), and space Used on your startup disk will be displayed, as seen in the following screen shot:
Simple ways to free space
You can employ any of the following tips to increase the free space available on your Mac OS X startup disk without altering your hardware.
Empty the Trash
As obvious as it may sound, some folks regularly Trash files but neglect to periodically empty the Trash. In Finder, select Finder > Empty Trash or, under Mac OS X 10.3 or later, you can also select Finder > Secure Empty Trash.
Do not use the Trash as a temporary storage area: only put an object in the Trash if you are sure it is no longer needed.
Some applications, such as iPhoto® and Mail, have their own Trash, spearate from the Trash seen in the Dock. Emptying the application’s Trash may delete its contents immediately or move its contents to your personal Trash, which you can then empty as noted above.
Archive old files
Archive — move, copy and delete, or backup and remove — files you do not use regularly to CD or another backup medium.
If you have not done so already, this is an excellent time to consider implementing a comprehensive backup and recovery solution.
Mac OS X 10.3 Panther® and later include a built-in function for creating compressed archives of files or folders. These archives are generally far smaller than the original files they contain, provided the original is not already in a compressed format. To use this function, see the following AppleCare® Knowledge Base document corresponding to the version of Mac OS X you are using:
Clean up system logs and temporary files
Follow the advice in our 'Running Mac OS X Maintenance Scripts' FAQ to regularly execute the Mac OS X maintenance routines that clean up System logs and temporary files created as part of the UNIX® underpinnings of Mac OS X.
Remove unused localization files
If you selected the Easy Install option when installing Mac OS X, localization files for over a dozen languages are installed. These files enable the Mac OS X interface to appear in a variety of languages. You can save roughly 200MB of disk space by removing unneeded localization files using the freeware utility Monolingual.
| Warning: | Be sure to thoroughly read the instructions before using Monolingual. Only use a version that is compatible with the version of Mac OS X you have installed. Never remove English localization files. Many applications require English and will not open if English is removed. |
Delete the Previous Systems folder from a prior Archive and Install
If you have performed an Archive and Install of Mac OS X, a Previous Systems folder was created containing your prior Mac OS X System folder. Once you are satisfied that your Mac is functioning properly after an Archive and Install, you can delete the Previous Systems folder as follows:
- Mac OS X 10.3 Panther® or later:
- Using your Admin account, drag the Previous Systems folder to the Trash.
- Type your Admin password when requested to authenticate this operation.
- Empty the Trash.
- Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar: See the AppleCare Knowledge Base document 'Mac OS X 10.2: How to Delete a Previous Systems Folder.'
Uninstall unused applications
If your Macintosh HD > Applications folder is cluttered with applications you are no longer using or trial software that shipped with your Mac that you do not intend to use, then uninstall them.
Delete old iTunes Library file backups
Recent versions of iTunes® create a backup of your current iTunes Library file whenever the iTunes application is updated. After you are satisfied that an iTunes update is performing nominally, trash old iTunes Library files with your Home > Music > Previous iTunes Library folder, then empty the Trash.
Remove old iOS device backups
Apple iOS® devices (iPad®, iPhone®, iPod touch®) automatically back up specific files and settings to your Mac whenever they are connected to your computer. The backups are saved in your Home > Library > Application Support > MobileSync > Backup folder. While you should retain your most recent backups from these devices, older backups can be deleted in the Devices pane of iTunes preferences. For details, see the following AppleCare Knowledge Base documents:
Trashed iDVD or GarageBand? Don't forget the loops and themes…
If you plan to uninstall iDVD® or GarageBand® by moving these applications' icons from the Macintosh HD > Applications folder to the Trash, be sure to also trash the corresponding iDVD or GarageBand folders within the Macintosh HD > Library > Application Support folder. These folders contain iDVD themes and GarageBand loops and instruments, respectively, that consume several gigabytes of disk space.
Uninstall Mac OS 9
If your PowerPC™-based Mac can only start up into Mac OS X and you have no need for Classic mode, you can uninstall Mac OS 9 to save additional space.
More ways to save space if you have a spare partition or second hard drive
If you have an available partition or a second hard drive, you can also save space on your Mac OS X startup disk with the following additional tips.
Move your iTunes Music folder to another disk or partition
To change the location of your iTunes Music folder, carefully follow the instructions in the AppleCare® Knowledge Base document 'iTunes for Mac: Moving your iTunes Music folder.' Additional information can be found in iTunes Help.
Laptop users may want to consider having two iTunes libraries: a small library of current favorites on their computer, while their complete library resides on an external hard drive. Utilities like iTunes Library Manager enable you to easily have multiple iTunes libraries you can use with your account.
You can investigate other solutions for managing multiple iTunes libraries by searching MacUpdate and VersionTracker.
Move your iPhoto Library folder to another disk or partition
To move the iPhoto Library folder to a new location, employ the instructions in the AppleCare Knowledge Base document from this list corresponding to the version of iPhoto you are using. Additional information can be found in iPhoto Help.
Laptop users may want to consider having two iPhoto libraries: a small library of current, favorite photographs on their computer, while their complete library, or archives of older photos are saved on an external hard drive. Utilities such as iPhoto Buddy and iPhoto Library Manager enable you to have multiple iPhoto libraries that you can use with your account.
You can investigate other solutions for managing multiple iPhoto libraries by searching MacUpdate and VersionTracker.
What about moving my Home or Users folder?
The UNIX underpinnings of Mac OS X make it possible to move either your Home folder or the entire Users folder to a different disk or partition. While this seemed to work well for some users in the early days of Mac OS X, it has become problematic with respect to Mac OS X Updates.
For example, we know of at least one Mac OS X Security Update that expected the Users folder on the Mac OS X startup disk. Those who had relocated Users to another partition had problems installing this update. Consequently, we do not recommend moving either your Home or Users folders to a different disk or partition.
Finding lost disk space
Freeing Up Memory On Mac
If you find your Mac OS X startup disk has become full unexpectedly:
- Check Console for clues. In particular, examine the various Console logs for large blocks of identical, repeating messages. Such blocks of repeating messages often indicate a runway process is logging excessively due to either a flaw in the process itself, its logging parameters, or a problem with your Mac. Excessive logging can result in log files growing without bounds.
- The utilities OmniDiskSweeper and WhatSize are great for finding large, invisible files. Be sure you understand the purpose of a large file before deleting it. In particular, Virtual Memory (VM) Swap files, located in the /private/var/vm directory, should not be deleted while your Mac is running. VM Swap files are created and released dynamically by Mac OS X.
System cleanup in one click
Few things are as frustrating as your Mac telling you it has run out of memory when you’re trying to be productive. But it’s even frustrating when you’ve ignored the problem for quite some time and your Mac’s limitations simply won’t let you put a solution on hold any longer.
- How to get rid of low memory notifications
Usually, a popup warning isn’t the first sign that something is amiss. You may have noticed that your Mac isn’t running as fast as it used to, with the fan louder than normal as if it’s struggling to carry a heavy load up a hill.
Although Macs are wonderful computers, like any other, they have limitations. Thankfully, there is plenty you can do to resolve this problem and get your Mac operating smoothly again.
Reduce memory usage with Setapp
Instead of manually deleting files, get Setapp. It not only removes the clutter but also gives you full control over memory usage.
How to Fix Your System Application Memory
Mac memory usage is often occupied by apps, even browsers like Safari or Google Chrome. In the most dire circumstances, your Mac will toss a warning at you: “your system has run out of application memory.”
Don't despair – it's solvable. The first thing to note is this is a natural issue; your Mac has a limited amount of RAM. Though more expensive Macs have more RAM, even they can butt against limitations when too many applications are running.
It may also be an app that is hogging all of your resources. This is especially true of older applications which haven’t been optimized for modern computer architecture. Websites may also be a culprit. Let’s discuss all these possibilities step by step.
How to check RAM usage on Mac
To check your RAM use on any Mac, take the following steps:
- Open Activity Monitor from your list of applications. You can do this in Mac’s control center, via the Finder in your Dock, or by pressing ⌘ + Space and typing Activity Monitor in the Spotlight.
- Toggle to the Memory pane in the Activity Monitor window
As you see in the above screenshot, Activity Monitor shows you all of your processes, sub-processes, and how much memory each is taking up. The most pertinent portion of the window is the bottom, where it shows you the total memory usage, and how it’s affecting your Mac.
A better way to monitor your Mac’s memory use is with iStat Menus. After installing the app, it makes a home in your Mac’s menu bar, and monitors just about everything, including memory, CPU, GPU, disks, and network usage.
You can choose which systems you’d like to monitor in the app itself. Only the items you’re monitoring will have an icon in your menu bar. A simple click on the menu bar icon surfaces a drop-down menu of how your Mac is performing at the time, and hovering over each graphic brings up a larger menu to inspect.
How to check CPU usage on Mac
Checking CPU use on your Mac is similar to the steps above for checking memory use. For Activity Monitor, you'd make sure to highlight the CPU section of the window. This will show you all the processes using your Mac's CPU at the time.
Similarly, iStat Menus has a CPU & GPU toggle just above the memory section. Activating that will add a CPU and GPU monitor to your Mac menu bar, which has the same interactivity as the memory icon and menu shown above.
But what creates CPU-hogging problems overall and how do they lead to slow Mac performance?
Every Mac has a processor which handles the computing of any task, from opening an app to editing photos. Processors differ in power (expressed in GHz) and efficiency (generally, newer processors are more efficient).
For example, a 9th Generation 2.2 GHz Dual-Core Intel Core i7 processor means that it has two i7 chips, each of which is able to process data at up to 2.2 GHz, and its the 9th iteration of that processor overall.
However, regardless of the power of your processor, if you throw too many tasks at it, it will start to slow because it’s trying to process too much information at once (try opening 100 Google Chrome tabs), creating a bottleneck. That’s why you can have applications not responding. So you need to do something about it.
App Tamer is perhaps the most powerful smart CPU manager out there. Not only does it show the exact CPU percentage and battery impact each process is taking from your Mac, it lets you create simple rules to prevent certain processes from hogging too much CPU.
To tame any app, just click on it in App Tamer (located in the menu bar), select “Slow down this app if it uses more than” and specify the exact CPU percentage.
How to free up memory on Mac
Knowing how to clear memory on Mac is important, especially if you have a Mac with limited resources. One option is using Activity Monitor:
- Open Activity Monitor on your Mac
- Select an app using a lot of memory
- Click the stop icon in the top bar
This is straightforward, but there's a better way. CleanMyMac X has an automated CPU and memory monitors built-in, which can give you a real-time view of memory usage in your Mac's menu bar. It also has a really quick and easy way to free up memory without digging through Activity Monitor and manually shutting down apps.
All you have to do is click the CleanMyMac X icon, select Free Up in the memory pane, and the app takes care of the rest! Oftentimes, it doesn't even shut apps down.
This is a quick fix, but CleanMyMac X takes it a step further in the app itself. Under the app's Maintenance section is an option to Free Up RAM, which helps you clear RAM on Mac. Once you've got this option selected, simply select Run at the bottom of the window, and CleanMyMac X will do a thorough scrubbing of your Mac's RAM, and clear unused files out of the way.
How to get rid of low memory notifications
Most apps are pretty good about how they use your Mac's resources. Having too many open or running in the background can severely limit what your Mac can handle, and is often why a Mac overheats or slows down.
Below we list a few tips to reduce high memory usage manually if you're experiencing unique warnings or issues.
Fix kernel_task, a high CPU usage bug
You may have noticed through Activity Monitor something called kernel_task absorbing a large amount of processing power. One of the functions of kernel_task is to help manage CPU temperature; you may find that your Mac fan is loud and always on, even if the device isn't hot to the touch.
That's because kernel_task usually performs this way when one or more applications are trying to use too much CPU. Unfortunately, one of the potential downsides is a Mac can overheat to such an extent that internal systems are damaged, sometimes irreparably.
Working through the following steps in this article is one way to avoid similar problems. If none of this work and kernel_task is still absorbing a high percentage of your CPU, then one or more of the following could be the cause:
- Cooling system inefficiency
- A failed or disconnected temperature sensor
- Another hardware issue, including a worn out batter
- Your System Management Controller needs a rest
If you're experiencing severe issues, Apple recommends a system management controller (SMC) reset. It's essentially a hard reset for your Mac, and should help your RAM and other hardware components start from scratch. Keep in mind you won't lose any data in this process.
Reduce memory usage in Finder

One common culprit for RAM issues is Finder, your Mac's file manager. If iStat Menus or Activity Monitor has highlighted Finder as using hundreds of MBs of RAM, there is an easy solution: change the default display for a new Finder window so it doesn't show All My Files:
- Click on the Finder icon in the Dock and click on the Finder menu, then select Preferences
- Click on General. Under 'New Finder windows show', click the dropdown menu and choose any option except All My Files
- Close Preferences, press Alt-Control, and click on the Finder icon in the Dock. Click Relaunch
Free Up Storage On Mac El Capitan
Finder will now relaunch with new windows opening at the option you selected in step two.
Improve Chrome's Task Manager
Chrome is a popular browser, but it's a resource hog! Chrome uses a GPU Process as standard, which means it speeds up the loading of web pages, which can be great except at times when your computer is struggling with insufficient RAM.
Here's how to make it better:
- Open Chrome on your Mac
- On the right side of the Chrome window, select the three-dot menu
- Select More tools
- Select Task Manager
- Select a Chrome process you'd like to kill
- Select End Process at the bottom right of the window
Here's another way to reduce Chrome's use of your Mac's memory:
- Open Chrome on your Mac
- On the right side of the Chrome window, select the three-dot menu
- Select Settings
- Scroll to the bottom of the page and select Advanced
- Scroll down to System, and toggle 'Use hardware acceleration when available' off
This will affect how Chrome runs on your Mac, and your experience won't be as smooth. You can also remove unused or unwanted Chrome extensions to help it use less resources on your Mac.
Get CMM X to free up space
Install CleanMyMac X and streamline the entire process of memory management on Mac. Clever memory usage control done for you.
Clean up other browsers
In every browser you use regularly, there are always going to be extensions and popups that take up space and use RAM. You can manage each one manually or use a tool such as CleanMyMac X to identify and delete them.
In the CleanMyMac X app is a section titled Extensions, which lists each extension you have for your browser or browsers. All you have to do is view the list of extensions, select the ones you no longer want, and remove them. It's really that simple!
Disable login items
Login items, browser extensions, and preference panes, such as Flash, are another common source of memory usage. Most of us have several installed that we rarely use, but which hog memory and reduce performance.
One way to do this is through System Preferences:
- From your Mac menu bar, select System Preferences
- Select Users & Groups
- Select Login Items
- Deselect items you no longer want active at login
Another way, one that is even quicker, is to employ CleanMyMac to identify and cleanup login items:
- Open CleanMyMac X
- Under Speed, select Optimization
- Select Login Items
You can remove all login items, or select the ones you'd like to remove individually on the right side of the window.
Freeing Up Memory In Vista
Disable desktop widgets
Older Macs running a version of macOS older than Catalina can disable widgets. Desktop widgets can provide a useful shortcut to apps you need to access fairly often. But they can take up processing memory that is slowing your whole Mac down. One way to close them completely is in System Preferences.
Go to Mission Control ➙ switch off the Dashboard
Declutter your desktop
Apple's built-in decluttering tool is handy for many. All you have to do on your cluttered desktop is right-click, then select Use Stacks. This places all of your desktop files into folders unique to their filetype, like Screenshots and Images.
A better way is to use Spotless, an app that gives you far more control over how your Mac is organized. It has several triggers for automated cleanup of files on your desktop, placing them wherever you see fit. It's particularly useful for power users who produce several files daily, but don't want to take the time to place each in a respective folder.

You can also select many files on your Mac desktop, and tell Spotless to tidy them up. You always have full control!
Schedule regular cleanups
Freeing Up Memory On Mac Air
Constant use of your Mac, or leaving it on all the time, will slow it down over time. Shutting it down and restarting is a traditional way of 'cleaning up' a computer.
We also like CleanMyMac X's scheduled cleanup feature. Telling the app when you'd like to perform a thorough cleaning up of your Mac's system is a method many prefer to shutting down and restarting often. It has the upshot of removing files and folders you no longer use, and cleaning up tasks that are slowing your Mac down behind the scenes. A simple shutdown may not do this.
Keeping your Mac in tip-top shape is critical. While we'd all like to think computers are brilliant little devices that can handle anything, they need some care, too.
All of the apps mentioned in this article help with taking care of your Mac, and protecting your investment. Best of all they're each free as part of a seven day trial of Setapp. Give it a try today!